
What is matter?
What is Matter? The answer to this question is here in this Science Section! Everything that has mass and volume (occupies space) in the universe is known as matter. Matter is made up of invisible nano particles. Hundreds of thousands of bricks form a building. Similarly, billions (or trillions or quadrillions) of invisible minute particles form a visible matter.
The size of these invisible minute particles are so tiny that it is beyond our imagination. It is about less than 1 nano metre (0.000000001 m).
If we breakdown a small piece of a matter (for example, an iron piece) continuously, we can obtain a visible dust of iron. Breaking the same further over and again, we can reach out the tiniest particle of the iron. Thus, billions or trillions of tiny particles particles together form a matter.
Some examples of matter:
- A tiny dust particle,
- mustard,
- pebbles,
- rocks,
- mountains,
- a drop of water
- ocean
- air,
- food,
- our belongings,
- everything that we see around us,
- all living things including us, humans,
- all non-living things in the world,
- planets,
- stars
- galaxies
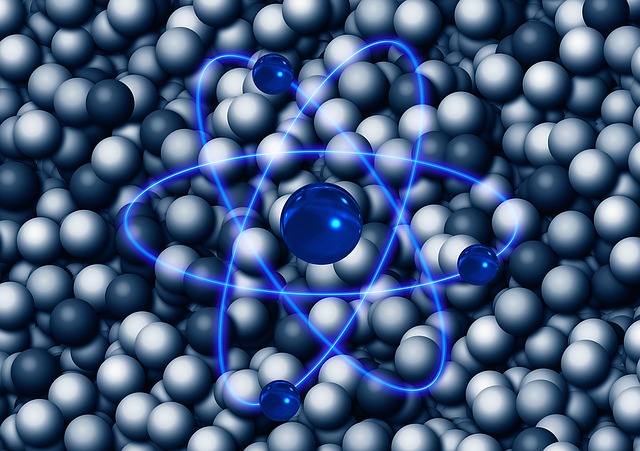
Particles (Atoms) of Matter 
Particles (Molecules) of Matter
In general, matter may be in any of the three states namely, solid or liquid or gas. It is found in other states too. They are, plasma and Bose-Einstein Condensate. But, we’ll be discussing the first three states alone in this article.
Solid
In general, the particles in the matter are bound by strong force of attractions between them. Since this force is the very strong in solids and the particles are tightly packed, solid matter gets a rigid shape. The particles inside the matter stay at a fixed position and vibrate up and down continuously.
Liquids
When compared to solids, the particles in liquids have weaker force of attraction and bonds between them. These particles vibrate and move continuously, thereby making the liquids flow. This why, the liquids get the shape of the container they are kept in.
Gases
The particles in gases have still weaker force of attraction and bonds among them. Hence, the gas particles move continuously at a faster rate in various directions. The gases don’t have specified volume. They can be compressed at high pressure and held in a small container.
Atoms and Molecules
The fundamental articles of a matter may be atoms or ions or molecules. If the matter is a pure element like iron or aluminium, the tiniest particles that form the matter are atoms. On the other hand, a compound is made up of molecules of two or more elements.


Be the first to comment