Microorganisms – Notes / Handout – Chapter-2 – CBSE Class-VIII
Microorganisms are tiny living organisms, which can be seen only with the help of microscopes. Some organisms like fungus that grow on the bread, can be seen with a magnifying glass. Microorganisms are also called microbes.
- Microbes may be:
- single-celled organisms (unicellular) like bacteria, some algae and protozoa (or)
- multicellular organisms like many algae and fungi.
Where do Microbes live?
They live in any type of environment like:
- soil
- water
- oceans
- air
- ice cold regions
- hot springs
- deserts and
- marshy lands
Types of Microorganisms
Microorganisms are classified into four major categories namely;
- Bacteria – Examples: E. Coli (Escherichia coli), Lactobacillus
- Fungi – Examples: Bread mould, Penicillium, Aspergillus
- Protozoa – Examples: Amoeba, Paramecium.
- Algae – Examples: Chlamydomonas, Spirogyra
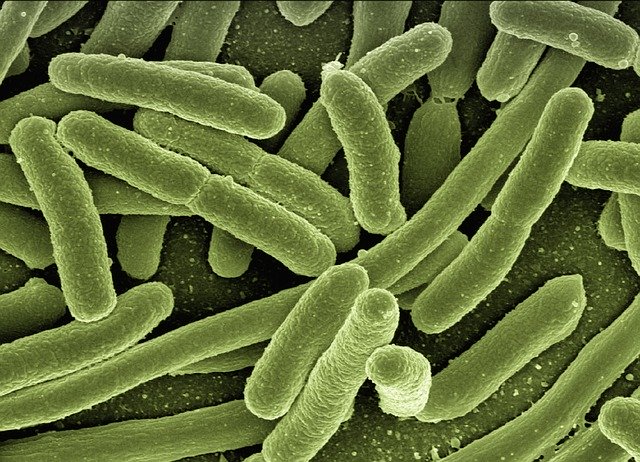
Coli – Bacteria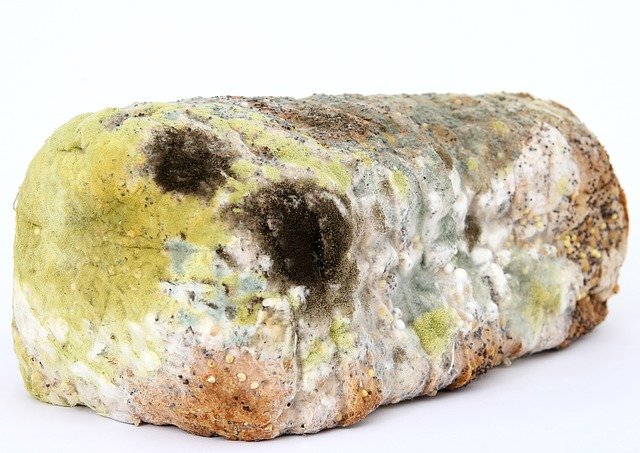 
Bread Mould – Fungi 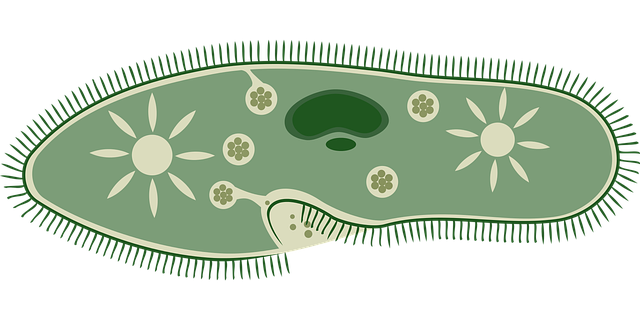
Paramecium – Protozoan
Viruses
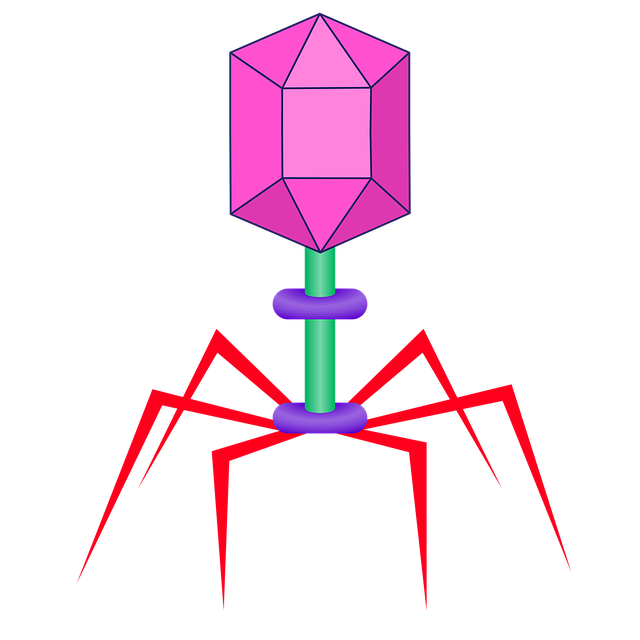
Bacteriophage – Virus 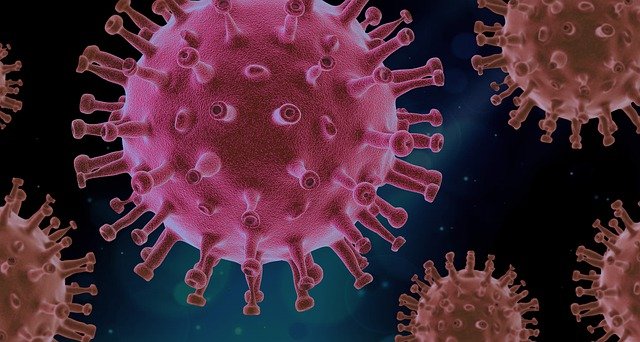
Corona – Virus
- Examples of Viruses: Bacteriophage, Corona
- Viruses are also microscopic but are different from other microbes. They are non-living in nature and become active only when they come in contact with a host.
- They reproduce only inside the cells of the host organism (bacterium, plant, or animal)
- They cause common ailments like cold, influenza (flu) and coughs
- Polio, chickenpox, measles and hepatitis-A are also caused by viruses

What is the study of microorganisms called?
The study of microorganisms is known as Microbiology.
Who is known as the father of microbiology?
Antony Van Leeuwenhoek is called the “father of microbiology”
Friendly Microorganisms
- Microorganisms are used to prepare:
- curd
- cheeze
- pickles
- bread
- cake
- alcohol
- medicines
- They are useful in cleaning up the environment.
- For instance, bacteria decomposes (breaks down) organic wastes like, vegetable peels, remains of animals, faeces in to harmless and useful substances.
- In agriculture, they increase the soil fertility by fixing the nitrogen.
Making of Curd
- The bacterium called lactobacillus promotes the fermentation of curd. It multiplies in milk and converts it into curd.
Fermentation
- Fermentation is the process of conversion of sugar into alcohol.
- Uses:
- Preparation of Food: Rava Idli, Bhatura, Dosa batter
- Commercial use of yeast: In order to produce alcohol, wine, acetic acid (vinegar), yeast is grown on natural sugars present in grains like barley, wheat, rice and crushed fruit juices.
Medicinal use of microorganisms
Antibiotics
- Antibiotics are medicines that kill or stop the growth of the disease causing microorganisms.
- They are produced from bacteria and fungi
- Streptomycin, tetracycline and erythromycin are made from antibiotic medicine like penicillin
- The source of these medicines is microorganisms
- Antibiotics are not effective against cold and flu. Because they are caused by viruses
- Antibiotics are mixed with the feed of livestock and poultry to check microbial infection in animals
- Used to control many diseases in plants
Vaccines
- Antibodies produced in the body fight and kill the invading microbes. When dead or weakened microbes are introduced in the body, the suitable antibodies fight and kill the bacteria or viruses
- Diseases like cholera tuberculosis smallpox and hepatitis can be prevented by vaccination
Increasing Soil Fertility
- Rhizobium bacteria fixes nitrogen from atmosphere to enrich the soil with nitrogen and increase its fertility. These are called biological nitrogen fixers.
- Example: cyanobacteria (blue green algae)
- Cleaning the environment
- Some microbes decompose the dead plants or animals and animal wastes and convert them into manure.
Harmful microorganisms
- Pathogens – Disease causing microorganisms
- Pathogens enter our body through the air we breathe, drinking water, food or by physical contacts
Communicable diseases
Diseases spread from an infected person to a healthy person through air, water, food or physical contact are called communicable diseases.
Common Diseases Caused by Microbes in Humans
- Bacteria cause tuberculosis (TB), cholera and typhoid
- Protozoa cause dysentery and malaria
- Viruses cause Polio, chickenpox, measles and hepatitis-A, cold, influenza (flu) and coughs
Microbial Diseases in Animals
- Anthrax is a disease caused by the bacterium (Bacillus anthracis) in humans and animals.
- Foot and mouth disease of cattle is caused by virus.
Microbial diseases in Plants
- Bacteria causes citrus canker
- Rust of wheat is caused by fungi
- Yellow vein or mosaic of bhindi (Okra) is caused by virus
- Carriers of disease causing microbes:
- Housefly
- female Anopheles mosquito (carries parasite of malaria called plasmodium) spreads malaria
- Female Aedes mosquito carries the dengue virus
Food Poisoning
- Some microorganisms grow on food and spoil it by releasing some toxic substances in it.
- Consumption of food spoilt by the microorganisms causes food poisoning.
- Spoilt food;
- emits bad smell
- has bad taste
- has changed colour
Food Preservation
- It is the process of saving food from getting spoilt by microorganisms.
- Substances used for preserving food are called preservatives. They stop or prevent the growth of microbes in foods.
- Preservatives
- Common salt (used in pickles, meat, fish)
- Edible oils and Acids like vinegar (used in pickles, vegetables, fruits, fish and meat)
- Sodium benzoate and Sodium metabisulphite (used in jams and squashes)
- Sugar (used in jams and jellies)
- Heat and Cold Treatments of Food
- Boiling (kills many microorganisms)
- Refrigeration (low temperature prevents the growth of microbes)
- Pasteurisation of Milk – The milk is heated to about 70o C for 15 to 30 seconds and then suddenly chilled and stored. This process prevents the growth of microbes. This process is called Pasteurisation.
- The process of Pasteurisation of milk was discovered by Louis Pasteur.
- Storage and Packing
- Usage of sealed air tight packs (to protect dry fruits and vegetables from the attack of microbes)
Nitrogen Fixation
- The bacterium Rhizobium lives in the root nodules of leguminous plants and convert nitrogen present in the atmosphere in to usable compounds of nitrogen.
- Also, some bacteria and blue green algae (Cyanobacteria) present in the soil fix the nitrogen.
- Plants absorb the usable form of nitrogen compounds through roots and use them for the synthesis of plant proteins.

Be the first to comment