
Short Notes – Science Handout – Light: Reflection and Refraction (Class 10 NCERT – CBSE)
Reflection of Light
Definition: Reflection is the bouncing back of light when it hits a smooth surface without passing through it. A highlight polishes surface (for instance, mirror), reflects most of the light falling on it.
Types of Reflection:
- Regular Reflection: Occurs when light reflects from a smooth surface (like a plane mirror), producing a clear image.
- Irregular (Diffuse) Reflection: Occurs when light reflects from a rough surface, scattering in different directions, forming no clear image
Laws of Reflection:
- Angle of incidence (i) = Angle of reflection (r).
- Incident ray, reflected ray, and normal to the surface lie in the same plane.
The above reflection laws are applicable to all types of reflecting surfaces (Plane, curved or spherical)
Types of Mirrors
- Plane Mirrors
- Curved (Spherical) Mirrors
- Concave Mirrors
- Convex Mirrors
Spherical Mirrors
- Key Terms and Definitions:
- Pole (𝑃): Geometric centre of the mirror.
- Centre of Curvature (C): The centre of the sphere the mirror is part of.
- Radius of Curvature (R): Distance between P and 𝐶.
- Focus (F): The point where parallel rays converge (concave) or appear to diverge (convex).
- Focal Length (f): Distance between P and F.
- Image Formation by Concave Mirrors:
- Position of Object and Image:
- Beyond C: Real, inverted, smaller, between F and C.
- At C: Real, inverted, same size, at C.
- Between C and F: Real, inverted, larger, beyond C.
- At F: Real, inverted, infinitely large.
- Between F and P: Virtual, erect, larger, behind mirror.
- Image Formation by Convex Mirrors:
- Object anywhere: Virtual, erect, diminished, behind the mirror.
- Mirror Formula and Magnification:
- Mirror Formula:
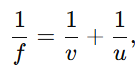
where f = focal length, u = object distance, v = image distance.
- Magnification (M):

Refraction of Light
- Definition: Refraction is the bending of light when it travels obliquely from one transparent medium to another. It’s caused due to a change in the speed of light, which varies from medium to medium.
- Key Terms:
- Incident Ray: The ray entering the medium.
- Refracted Ray: The ray bent inside the medium.
- Normal: A perpendicular line to the interface of the two transparent media at the point of incidence.
- Angle of Incidence (i): Angle between incident ray and normal.
- Angle of Refraction (r): Angle between refracted ray and normal.
- Laws of Refraction:
- The incident ray, refracted ray, and the normal to the interface of two transparent media at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
- Snell’s Law:
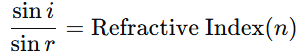
- Refractive Index (n):
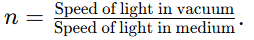
Higher n: Optically denser medium.
Lower n: Optically rarer medium
Lenses
- Types of Lenses:
- Convex Lens: Converges light; thicker at the center.
- Concave Lens: Diverges light; thinner at the center.
Image Formation by Lenses:
- Convex Lens:
- Object at infinity: Real, inverted, point-sized, at F2.
- Beyond 2F1: Real, inverted, smaller, between F and 2F2.
- At 2F1: Real, inverted, same size, at 2F2.
- Between F1 and 2F1: Real, inverted, larger, beyond 2F2
- At F1: No image (rays parallel).
- Between F1 and optical centre: Virtual, erect, larger, same side as object.
- Concave Lens:
- Object at any position: Virtual, erect, diminished, same side as object.
Convex Lens:
- Lens Formula
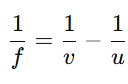
- Power of a Lens (P)
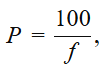
where f is in cm and P is in dioptres (D).
- Total Internal Reflection (TIR):
- Occurs when light travels from a denser to a rarer medium at an angle greater than the critical angle.
- Applications: Fibre optics, mirages.
- Dispersion of Light:
- Splitting of white light into its spectrum when passed through a prism.
- Applications:
- Concave Mirror: Solar cookers, shaving mirrors, telescopes.
- Convex Mirror: Vehicle rearview mirrors, street lights.
- Convex Lens: Magnifying glasses, cameras, projectors.
- Concave Lens: Corrective glasses for myopia (short-sightedness).


Be the first to comment